Audio Capture Modes
TuneBlade captures system wide audio and streams it to AirPlay receivers. (It can also capture audio from any audio endpoint through 'Specific Endpoint' capture mode. Refer 3 below.)
TuneBlade can capture audio in three different ways:
1. Direct Loopback
In Direct Loopback capture mode, TuneBlade captures audio from the default audio-out device. No kernel driver installation is required. This is the default capture mode. It doesn’t need any configuration, and works out of the box. However, when an application is playing premium or protected audio content such as DRM protected files, audio capture is of degraded quality. Switching to Virtual Device Loopback audio capture mode will solve this issue.
2. Virtual Device Loopback
In this capturing mode, a pair of virtual audio devices are added to your PC. One of the virtual devices is an audio-out endpoint, and the other one is a line-in endpoint. The nifty thing about this pair of virtual devices is that they are digitally connected i.e. whatever audio goes into the virtual audio-out can be captured from the virtual line-in device of the pair!
TuneBlade is compatible with any third party software providing this functionality and has been tested to work with VB-Cable (donation ware) by VB-Audio and Virtual Audio Cable (Paid) by Eugene Muzychenko.
When to switch to Virtual Device Loopback?
By default, TuneBlade is configured to capture using Direct Loopback as it doesn’t require any third party virtual sound drivers. You should switch to Virtual Device Loopback if:
-
If you are experiencing degraded audio quality being played over AirPlay. The degraded sound quality has a characteristic of sounding like it has non-existent bass and treble, and sounds as if playing at a very low sampling rate.
-
If your system’s default sound device doesn’t allow audio capture when it is muted. In Direct Loopback mode, TuneBlade will mute your local PC speakers when it is streaming audio. A few sound devices doesn’t allow capturing audio when muted.
-
If you use pro-audio applications such as Digital Audio Workstations (DAW), then it is likely that the 'Direct Loopback' capture mode will not work as these applications can take exclusive control of the endpoint. Using Virtual Loopback with VAC is recommended in this case.
Changing Audio Capture mode to Virtual Device Loopback
In this example, Virtual Device Loopback using VB-Cable is demonstrated.
-
Step 1
Download and Install VB-Cable from the VB-Audio website.
-
Step 1.1
Go to the VB-Audio website and download VB-Cable Virtual Audio Device.
-
Step 1.2
A zip file will be downloaded. Unzip it, and run the setup program in administrative mode. If you're running 32-bit Windows, run VBCABLE_Setup.exe, or for 64 bit OS run VBCABLE_Setup_x64.exe.
-
Step 1.3
Reboot after installation is complete.
-
Step 1.1
-
Step 2
Run TuneBlade, or if it is already running, restart it. Go to TuneBlade’s settings window by pressing the settings button on the interface.
-
Step 3
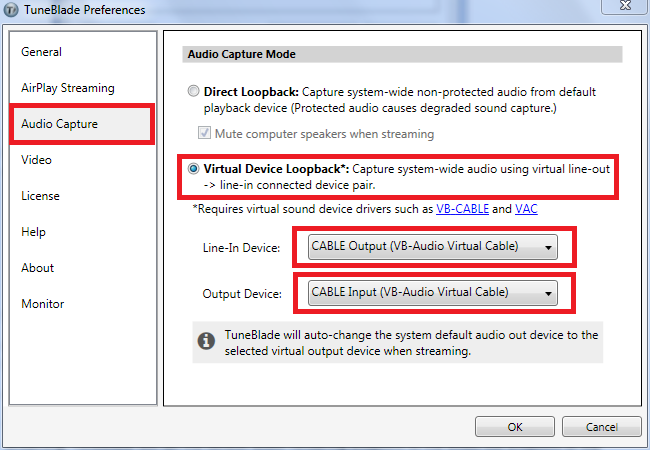
Select the ‘Audio Capture’ tab. Now select Virtual Device Loopback as the capturing mode. For the “Line-In Device” option, select “Cable Output (VB-Audio Virtual Cable)” and for the “Output Device” option select “Cable Input (VB-Audio Virtual Cable)”.
-
Step 4
Press Ok.
This gives TuneBlade the information about the virtual connected devices on your PC. While streaming, TuneBlade will set the default audio rendering endpoint to the audio out endpoint of the virtual cable so that the system wide audio is directed to this endpoint and TuneBlade can capture the audio from the other end of the virtual cable. Once you stop streaming, TuneBlade will switch the default endpoint back to your local device so that you can now hear audio on your PC speakers.
VB-Cable is a donationware software. If you find VB-Cable useful, it is recommended to make a donation to VB-Audio on their website.
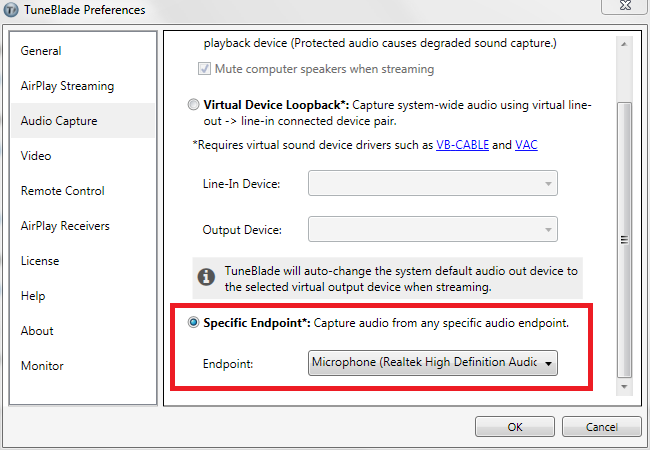
3. Specific Endpoint
In Specific Endpoint capture mode, TuneBlade captures audio from any available audio-in or audio-out endpoint using Windows Audio Session API (WASAPI). For instance, audio from Mic-In or Line-In can be captured and transmitted on AirPlay.